The Evolution of Software Economics: From Traditional Models to Cloud Computing
Introduction
Software economics plays a crucial role in project management, influencing cost structures, resource allocation, and scalability. As businesses increasingly rely on digital tools to streamline operations, understanding the evolution from traditional software models to cloud computing becomes essential. This transformation has reshaped how organizations develop, deploy, and manage software projects, directly impacting efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness.
The software industry has seen a fundamental shift from the early days of expensive, locally hosted solutions to the modern, cloud-based models that enable seamless scalability and cost efficiency. This evolution has not only affected businesses but has also changed consumer expectations regarding accessibility, performance, and flexibility. By examining this transformation in detail, we can better understand the underlying principles driving software economics today and their implications for project management.
Main Content
Core Concepts with Real-World Examples
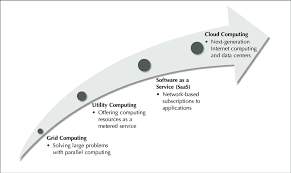
The evolution of software economics revolves around fundamental shifts in pricing models, deployment strategies, and operational efficiencies. Traditionally, businesses relied on purchasing perpetual licenses for software, meaning they paid a high one-time cost to use the software indefinitely. This model was common for enterprise solutions like Microsoft Office and Adobe Photoshop, requiring substantial upfront investments and ongoing maintenance costs.
However, as businesses grew and required greater flexibility, new economic models emerged. Subscription-based services like Software as a Service (SaaS) replaced one-time purchases with recurring fees, significantly lowering entry barriers. Companies such as Google and Microsoft transitioned to SaaS models (Google Drive, Microsoft 365), offering continuous updates and cloud-based storage instead of requiring users to manage software installations.
Another key shift was the introduction of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS). Companies no longer needed to invest in expensive IT infrastructure, as cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure enabled them to rent virtualized computing power. This transition has allowed startups and enterprises alike to scale operations efficiently without the burden of large capital expenditures.
How Leading Companies Manage Projects
1. Tesla
Tesla utilizes AI and data-driven project management to enhance innovation and production efficiency. By leveraging automation, predictive analytics, and agile workflows, Tesla maintains a competitive edge in the electric vehicle industry. Their Gigafactories, for example, operate using AI-driven robotics to optimize manufacturing and reduce waste.
2. Google
Google implements Agile and DevOps methodologies to streamline software development and cloud services. Google Cloud, for instance, relies on Kubernetes and containerized applications to ensure seamless deployment and scalability. Google's project management culture fosters rapid iteration and experimentation, which has enabled it to dominate search, AI, and advertising industries.
3. Microsoft
Microsoft integrates Scrum frameworks into its Azure cloud solutions and enterprise software development. By embracing Agile methodologies, Microsoft rapidly develops and deploys new features across its product lines, including Windows and Office 365. Microsoft's DevOps culture ensures continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD), enabling faster software releases with minimal disruptions.
4. Amazon
Amazon applies Six Sigma and Lean principles to optimize supply chain management and cloud infrastructure. AWS follows a customer-centric approach, ensuring high availability and performance for its cloud services. Amazon's fulfillment centers operate using AI-driven logistics, improving inventory management and delivery speed.
5. Toyota
Toyota pioneered Lean project management, ensuring minimal waste and high productivity in manufacturing. The Toyota Production System (TPS) emphasizes continuous improvement (Kaizen) and just-in-time (JIT) inventory management. These principles have made Toyota one of the most efficient automotive manufacturers globally.
6. IBM
IBM leverages AI-driven project management to enhance decision-making and automate workflows. IBM Watson, for example, provides predictive analytics and AI-powered automation to assist businesses in optimizing operations. IBM also incorporates blockchain technology to improve security and transparency in financial and supply chain management.
7. JPMorgan Chase
JPMorgan Chase uses Agile methodologies to develop and deploy fintech solutions rapidly. The bank invests heavily in AI and data analytics to enhance risk management, fraud detection, and customer experience. Their cloud-based infrastructure ensures secure and efficient banking services.
8. Netflix
Netflix implements DevOps practices to ensure seamless content delivery and service uptime. The company's cloud-native architecture, hosted on AWS, allows it to scale dynamically based on user demand. Netflix's recommendation algorithms rely on AI to personalize content, driving user engagement and retention.
Tools and Strategies in Project Management
1. Agile and Scrum
Agile project management promotes iterative development, enabling teams to adapt to changing requirements efficiently. Scrum, a subset of Agile, structures work into sprints, allowing for continuous improvement and faster delivery cycles. Companies like Microsoft and Google use Scrum frameworks to manage software development projects.
2. DevOps
DevOps integrates development and operations teams to enhance collaboration, automate deployments, and improve software quality. CI/CD pipelines ensure that code updates are tested and deployed seamlessly. Organizations like Netflix and Amazon use DevOps to maintain high availability and performance.
3. Lean and Six Sigma
Lean project management focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency, while Six Sigma emphasizes process improvement and defect reduction. Toyota’s manufacturing excellence is a prime example of Lean principles in action, while Amazon applies Six Sigma methodologies to optimize supply chain logistics.
4. AI-Driven Project Management
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing project management by predicting risks, automating scheduling, and optimizing resource allocation. AI-powered tools like IBM Watson and Google’s AI-driven analytics platforms enhance decision-making and project execution.
Conclusion
The transition from traditional software models to cloud computing has significantly influenced project management strategies across industries. Businesses now leverage Agile, Scrum, DevOps, and AI-driven methodologies to enhance productivity, efficiency, and innovation. Companies such as Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Tesla have successfully implemented these strategies to remain competitive in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
Looking ahead, the integration of AI, automation, and edge computing will continue to revolutionize software economics. As businesses strive for greater efficiency, cloud-based solutions will become even more sophisticated, enabling real-time collaboration, intelligent automation, and enhanced security. The future of software economics will be shaped by emerging technologies that drive cost efficiency, scalability, and innovation in project management.
Understanding these evolving trends is crucial for organizations and professionals looking to stay ahead in a competitive digital economy. By embracing new tools, methodologies, and economic models, businesses can optimize t
heir project management strategies and drive sustainable growth in the modern era of cloud computing.


Comments
Post a Comment